How to Prevent Sun Protection
We often talk about sunscreen, but what is it? In addition to the visible light (VIS) in daily life, there are also ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR), which are easy to be ignored, but it has been affecting us silently. Among of them, ultraviolet rays have the most significant damage to human skin.
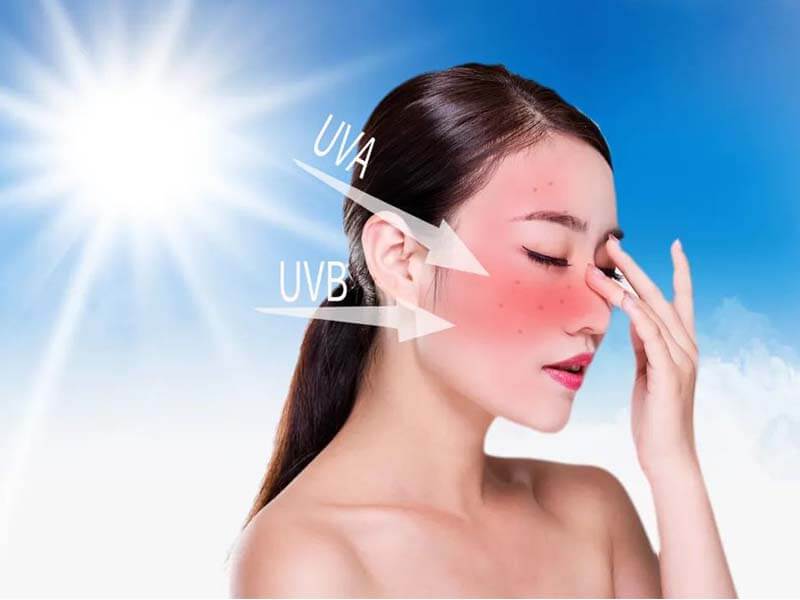

Types of UV rays
Ultraviolet rays in sunlight are mainly divided into three types according to their wavelengths: long-wave ultraviolet (UVA, 320-400nm), medium-wave ultraviolet (UVB, 280-320nm) and short-wave ultraviolet (UVC, 180-280nm). Among of them, UVC is almost completely absorbed when passing through the ozone layer, and only UVA and UVB reach the ground, accounting for 95% and 5% of the total, respectively.
The damaging effects of UV rays on the skin
UVB in ultraviolet rays acts on the epidermis, causing skin reddening, severe sunburn and even peeling after sun exposure; UVA can penetrate to the superficial layer of the dermis, mainly causing skin darkening and photoaging. At the same time, UVB and UVA in sunlight are also important pathogenic factors of non-melanotic and melanotic skin cancer.

What does sunscreen work include?
1. General protection, First of all, avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight at the time when the sunlight is the most intense (10:00-14:00); if you go out, you need to wear sunglasses, use an anti-ultraviolet umbrella, and wear sunscreen clothing (dark and light colors are better). ), wear a wide-brimmed hat, and try to avoid direct sunlight on the skin.
2. The ideal sunscreen agent for sunscreen should be able to prevent both UVA and UVB. In life, sunscreen agents with different SPF should be selected according to different seasons, weather conditions, and skin characteristics of different ages; and sunscreen must be 20- Apply for 30 minutes, about 2 mg per square centimeter, and reapply once every 2 hours.
3. Eat more fruits and vegetables for sunscreen foods, especially foods rich in vitamin C and vitamin E with antioxidant effects. Avoid or reduce the intake of light-sensitive foods, such as lettuce, fennel, amaranth, shepherd's purse, celery, radish leaves, spinach, coriander, rape, figs, citrus, lemon, mango, pineapple, etc.
4. Repair after sun exposure If you accidentally get sunburned, be sure to take advantage of the golden repair period of 6 to 8 hours after sun exposure for quick first aid. The first is to lower the skin temperature, and you can choose soothing sprays or wet compresses; the second is to strengthen repair and moisturizing; the third is to pay attention to your daily routine and avoid staying up late and anxiety. If there is no relief after two or three days of self-help, go to the hospital in time. Intensive hydration and nourishing repair work should be done at night.